Prof. Dr P R Goyal
Mobile-+919810506571
Email-pawanrajdr@gmail.com
For APPOINTMENTS
Mr. Akshat Upadhyay- 08273716142
SALUBRITY CLINICS
(Visible Effects Of Good Health)
(A unit of ITHIKA HEALTH SCIENCES LLP)
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
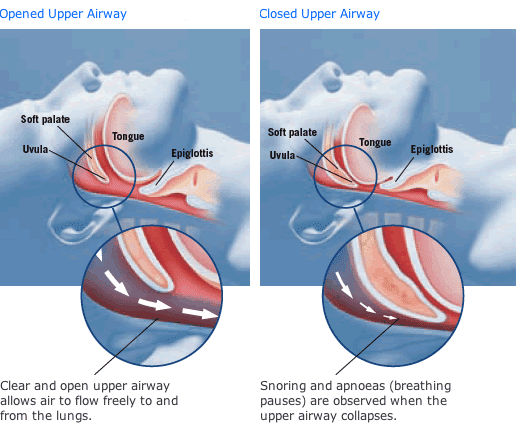

Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is a sleep disorder characterized by abnormal pauses in breathing or instances of abnormally shallow breathing, during sleep. Each pause or cessation in breathing is called an apnea, can last from a few seconds to minutes, and may occur 5 to 30 times or more an hour. Similarly, each abnormally low breathing event is called a hypopnea. Sleep apnea is diagnosed with an overnight sleep test called a polysomnography, or "sleep study".
There are three forms of sleep apnea: central (CSA), obstructive (OSA), and complex or mixed sleep apnea (i.e., a combination of central and obstructive) which can be easily differentiated with a sleep study. Treatment for all three varies. Regardless of type, an individual with sleep apnea is rarely aware of having difficulty breathing, even upon awakening. Sleep apnea is recognized as a problem by others witnessing the individual during episodes or is suspected because of its effects on the body. Symptoms may be present for years (or even decades) without identification, during which time the sufferer may become conditioned to the daytime sleepiness and fatigue associated with significant levels of sleep disturbance. There is significant fall in oxygen levels in association with apneas & hypopneas leading to various adverse effects on the human body like hypertension (increased blood pressure), increased risk of myocardial infarction, acute coronary syndrome, heart failure and stroke, elevated blood glucose, decreased HDL etc.